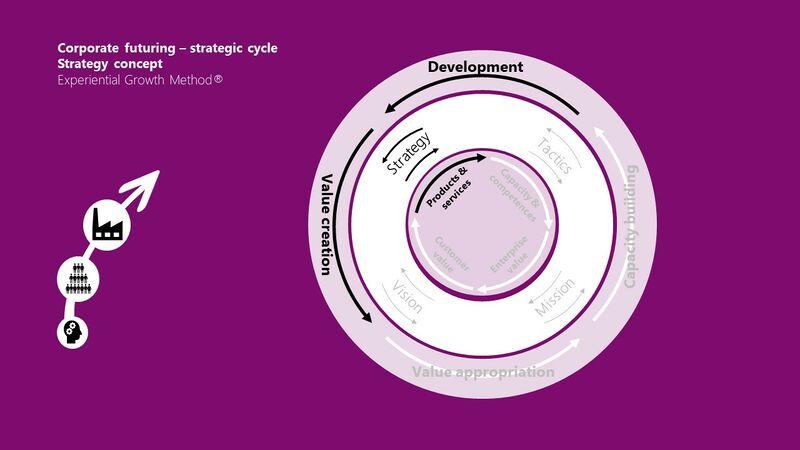
Strategic cycle: strategy
Chapter 4 - Corporate futuring
Previous page: Strategic cycle: vision - Stategic cycleː strategy - Next page: Strategic cycle: tactics
Back to Book content or directly to Main Page
.
Welcome to the Strategic cycle: strategy page
.
Change (or development), as the core concept of the 'strategic'-driven strategy
.
One can understand change as adapting to new situations or circumstances. This involves adjusting to new environments, processes, systems, or relationships within an organisation or one's personal life. External factors can drive change, such as technological advancements, market shifts, or regulatory changes, or it can be initiated internally, such as when an organisation decides to implement a new strategy or process.
.
The short story: What exactly is strategy?
Managing change effectively is essential for individuals and organisations to adapt and thrive in a constantly changing world. This can involve identifying the need for change, developing a plan, communicating the change to stakeholders, and supporting individuals as they adjust to the new situation.
Effective change management requires a clear vision, strong leadership, and effective communication. It also requires a willingness to embrace and adapt to new ideas, approaches, and working methods. By managing change effectively, individuals and organisations can navigate challenges and emerge more robust and resilient.
Product and service innovation is essential for your business to remain competitive and relevant in today's fast-paced and rapidly changing market environment. In addition, innovation can help your company create value for customers. Product innovation refers to introducing a new product or an improved version of an existing product. It can include introducing new features, improving performance, or adding new functionality to a product. Product innovation can be driven by customer needs and preferences, technological advancements, or a desire to differentiate the product from competitors. Service innovation refers to introducing a new service or an improved version of an existing service. Service innovation can be driven by factors similar to product innovation, such as customer needs and preferences, technological advancements, or a desire to differentiate the service offering from competitors. In addition, service innovation can involve the development of new business models or the introduction of new technologies to improve the delivery of a service.
Organisational development is a field of research and practices dedicated to increasing your organisations' effectiveness, productivity, and vitality. OD aims to improve your organisation's ability to adapt and respond to a rapidly changing environment by improving processes, systems, and structures that lead to better outcomes for the organisation, your employees, and all your stakeholders. OD interventions can take many forms, including training, coaching, process consultation, and organisational design.
.
Definition
The art and science of planning and marshalling resources for their most efficient and effective use. The term is derived from the Greek word for generalship or leading an army.
Strategy is the overall campaign plan, which may involve complex operational patterns, activity, and decision-making that lead to tactical execution.
A method or plan chosen to bring about a desired future, such as achievement of a goal or solution to a problem.
A careful plan or method for achieving a particular goal usually over a long period of time.
The skill of making or carrying out plans to achieve a goal.
.
Origin
Greek stratēgia generalship, from stratēgos
.
Synonyms
Arrangement, blueprint, design, game, game plan, ground plan, master plan, program, project, road map, scheme, plan, system
.
Related words
Collusion, conspiracy, plot; contrivance, device, gambit, manoeuvre, ruse, stratagem, subterfuge, trick; counter plan, counterstrategy; means, tactic, technique, way; procedure, protocol; conception, idea, project, proposal, specific(s), specification(s); aim, intent, intention, purpose; diagram, formula, layout, map, pattern, platform, policy, recipe, setup
.
In warfare
Coordinated application of all the forces of a nation to achieve a goal. In contrast to tactics, strategy's components include a long-range view, the preparation of resources, and planning for the use of those resources before, during, and after an action. The term has expanded far beyond its original military meaning. As society and warfare have steadily grown more complex, military and non-military factors have become more and more inseparable in the conduct of war and in programs designed to secure peace. In the 20th century, the term grand strategy, meaning the art of employing all the resources of a nation or coalition of nations to achieve the objects of war (and peace), steadily became more popular in the literature of warfare and statecraft.
.
Dive deeper
.
The dynamic & triangulated view on strategy
.
Strategy dynamics
|
.
Overall, your company's STRATEGY must be able to:
- produce the right products & services
- A product is a tangible item that your company produces and sells to customers. A service is an intangible offering that your company provides to its customers. You can sell both products and services or focus on just one or the other.
- while at the samen time, develop the enterprise
- Enterprise development is the process of your enterprises' (re-)creation and growth. This development can involve various activities, such as looking for financial assistance, training and education, business planning, or creating access to markets and networking opportunities. The goal of enterprise development is to become more sustainable, which can contribute to economic growth.
- and value creation for all stakeholders.
- Value creation aims to create long-term, sustainable value for all stakeholders, including customers, employees, shareholders, and society. Value creation refers to the various ways in which your company generates value for all its stakeholders. This can include creating value for customers through its products or services and creating value for shareholders and employees by providing a positive and fulfilling work environment. There are many different ways that your company can create value, and the specific strategies will depend on the industry in which you operate, your target market and your overall business model. Some common ways that companies create value include:
- Developing innovative products or services that solve problems or meet the needs of customers in a unique or better way
- Leveraging technology or other competitive advantages to increase efficiency and reduce costs
- Expanding into new markets or entering into strategic partnerships to increase revenue and reach
- Investing in research and development to drive innovation and stay ahead of competitors
- Building strong brand recognition and customer loyalty through excellent customer service and high-quality products or services
- Value creation aims to create long-term, sustainable value for all stakeholders, including customers, employees, shareholders, and society. Value creation refers to the various ways in which your company generates value for all its stakeholders. This can include creating value for customers through its products or services and creating value for shareholders and employees by providing a positive and fulfilling work environment. There are many different ways that your company can create value, and the specific strategies will depend on the industry in which you operate, your target market and your overall business model. Some common ways that companies create value include:
.
.
The results of the 'strategy'-driven strategic flow
When your company invests tangible and intangible resources with strategy in mind, it tends to end up with the following:
- customer value when there is an OUTSIDE-IN mentality
- Customer value is the perception of a customer's worth of your products or services. It is determined by the extent to which the product or service meets the customer's needs and expectations relative to the price they are paying for it. Customer value is essential because it can help your company determine how much to charge for its products or services. It can also help the company understand what its customers are looking for in terms of quality, features, and benefits. In general, the higher the customer value, the more likely a customer is to make a purchase and continue doing business with your company.
.
- or value creation when there is an INSIDE-OUT mentality.
- Value creation aims to create long-term, sustainable value for all stakeholders, including customers, employees, shareholders, and society. Value creation refers to the various ways in which your company generates value for its stakeholders. This can include creating value for customers through its products or services and creating value for shareholders and employees by providing a positive and fulfilling work environment. There are many different ways that your company can create value, and the specific strategies will depend on the industry in which you operate, your target market and your overall business model.
.
Two approaches about strategy
.
1. Strategy with an 'OUTSIDE-IN' (action) orientation
Overview
In this situation,
- while capabilities and competences is what we hope for,
- products & services is the critical step, and
- more than we wish for, we end up with (creating) customer value.
.
.
Dynamic process view
- First action (OUTSIDE).
- (When the enterprise creates products & services),
- value creation is the (next) big thing.
- The action step following this is value appropriation.
- Second focus (INSIDE).
- (Part of) these resources are converted to enterprise value,
- with which the organisation tries to create customer value.
- The hope is
- that this cycle will lead in a natural way to the right capabilities & competencies, but but to make this hope come true,
- (new) products & services are the critical step to shift the mindset from strategy to tactics.
.
Areas af concern
As you will have noticed, capabilities & competences, are nowhere in this situation
.
2. Strategy with an 'INSIDE-OUT' (focus) orientation
Overview
In this situation,
- while value appropiation is what we hope for,
- customer value is the critical step, otherwise
- we end up with (continuous) value creation.
.
.
Dynamic process view
- First focus (INSIDE)
- Strategic considerations guide the organisation towards specific products or services.
- Therefore, investments are made in capabilities and the competencies of employees.
- Second action (OUTSIDE).
- These rich intellectual resources enable enterprise development.
- If this enterprise strategy is correct, this leads to value creation.
- The hope is
- that this cycle will lead in a natural way to value appropriation, with the trap of operational excellence mission thinking,
- but customer value is the critical step, because it sucks the energy back into the organisation.
.
Areas of concern
As you will have noticed, enterprise value, nor capacity building are nowhere in this situation.
.
General concern
.
More important, capacity building is not present in the action- (outside-in) nor the focus (inside-out) situation..
.