Corporate futuring
Chapter 4 - Corporate futuring
Corporate futuring - Next page: Value realisation
Back to Book content or directly to Main Page
.
Welcome to the Corporate futuring page
.
Can you only see, at first sight, a cross, giving you a blocking feeling? Strategy can be overwhelming.
- Did you notice the inside-out flow shaping outside-in?
- This relationship represent the future of your venture.
.
Corporate futuring has three distinct steps:
- What is the situation you are in now?
- Externally (context)
- Internally (thinking, doing, organising, ...)
- What are the possible directions to go?
- What is your next step to take?
.
Again, Corporate futuring isn't a linear process toward a "desired growth KPI." All the elements on this and the following pages are stepping stones and resources to help you to see the connections between what is happening in your organisation and structure your strategic thinking about your organisation's future.
.
The story: About Strategy
Essay | Guido Van Nuffelen | 2025
.
Strategy
The best definition I know of strategy is still that of Simonne Vermeylen:
Strategy is making those decisions that make future decisions possible.
Of course, that also means that decisions can be made that make future decisions impossible. They can close doors.
What we can say with certainty is that homo economicus, the omniscient and independent decision maker, does not exist. We open and close doors consciously and unconsciously. We make decisions based on the context in which we live.
The present determines our position, but indeed also past action and thinking, because the past sets us at the point where we are now, with closed and opened doors.
.
It starts in 1632
John Locke
John Locke was born in Wrington near Bristol, England, on August 29, 1632.
Locke read Descartes during his studies and saw the great French philosopher as a viable alternative to the Aristotelianism he had learned at Oxford. In his work An Essay Concerning Human Understanding, he adopted Descartes' ideas as part of his thinking. According to Locke, every person is born as a "tabula rasa" or a blank slate. A person starts with an empty 'mind', and experiences and impressions fill the head.
He makes the unwritten natural law the foundation of formal constitutional law and the social contract. This forms the basis of his plea for popular sovereignty, the idea that the monarch or government must reflect the people's will.
"We the People," the opening words of the preamble to the U.S. Constitution, emphasize the centrality of popular consent. They were heavily influenced by John Locke's works, which reached America.
.
The core elements of Locke's philosophy are:
- Separation of powers
- Protection of property (including life, liberty and estate)
- Importance of impartial justice
Locke's ideas about natural rights, the social contract, the separation of powers, and the role of government resonate strongly with the founders of the first constitution. They designed a government dedicated to protecting and preserving individual liberties.
His defence of religious tolerance also significantly influenced the drafters of the American Constitution. Locke's 'Letter Concerning Toleration' advocates the separation of church and state and claims that the government may not impose religious practices or dictate beliefs.
This makes the United States a haven for people with different (religious) beliefs, emphasizing the principle that (religious) beliefs must be able to flourish free from government interference.
All this paves the way for economic liberal thinking.
.
Adam Smith is for economic liberalism, which John Locke did for political liberalism, namely building the philosophical foundations on which others will build a liberal tradition. The broad appeal of Smith's economic theories of free trade, division of labour, and the principle of individual initiative help to obscure a great deal of political liberalism in his work. Far from being a laissez-faire doctrinaire, Adam Smith aims to show that a liberal policy can enjoy the benefits of individual liberty and a free market economy.
Adam Smith's assumptions are:
- Economic growth depends on capital accumulation
- Economy works best through the interaction of selfish individuals
- Freedom implies free competition, free movement, free movement of capital, and freedom from government intervention
.
John Stuart Mill, philosopher, economist, journalist, political writer, social reformer and Liberal Member of Parliament, is one of the most famous figures in the pantheon of liberal theorists and the greatest Victorian liberal thinkers. A key aspect of his new political thought is his concern to combine the democratic demands of government accountability with a role for an elite of educated individuals, independent intellectuals and public moralists like himself.
John Stuart Mills assumptions are:
- Society is responsible for protecting its citizens, but should not interfere with the rest
- True freedom is the right to take care of yourself
- The basis of economics is competition
- Workers can participate in the capital of factories
.
For Europe this translates into a Calvinist way of life that results in the Golden 17th century:
- Since no one has certainty about his salvation and personal actions are not sufficient for this, the Christian needs strict fidelity to the creed and the dogmas
- A strong brake on free thinking and free research is desirable for this
- The individual bears responsibility for the way in which he deals with the inscrutability of the decree of God
- No government can decide on this in place of the citizen
.
This is the start of the neo-liberal era with the 'growth idea' as the main driver.
.
It also started in 1632
Baruch Spinoza
Baruch Spinoza was born in Amsterdam on 24 November 1632.
Spinoza is a perceptive observer who realises that man is not rational. Although he longs for a better world, he is very aware that a 'manageable society' is an illusion.
At an early stage, he resists the idea of God's election of the Jewish people, the divine origin of the Bible, and the image that God would be a human form. He resists fear and powerlessness but also permanent struggle and rivalry. It does matter to society what your motives are, whether you have good or bad intentions.
He writes a magnum opus on Ethics and treatises on politics. His texts are pleasantly modern. Below, you will find some core ideas:
Context
- Man is part of nature. This is incompatible with an aristocratic electness
Freedom
- When people can do what they are capable of, they can come into their power. This is necessary for science, trade and prosperity
Creativity
- No one can determine in advance what creativity is capable of
Strength & Power
- ‘Potentia’ is the strength every human being possesses. ‘Potestas’ is the power that results from the political system. It is a power that can hold others in its grip
Superstition
- Superstition arises when people no longer see the relationships that determine reality and therefore stray from science
Science
- Science and philosophy provide valid statements of truth, the (holy) scripture is not a source of scientific knowledge
- He asks himself whether you can claim the right in a democratic system not to have to come into contact with certain critical scientific content
Politics
- The aim of politics is not to rule over people and to keep them under control and subordinate with fear, but on the contrary to free them so that they can express themselves without harming themselves and others
- Democracy is the best form because it allows the ‘potentia’ of every citizen to be developed. Tyranny goes against this. The power of the ruler is great, but the strength of the citizens is thwarted
Moral awareness
- Moral life is not a lonely task. Fellow human beings are important to everyone. Only together with others can a person fully develop
- People influence each other, but from others one accepts only what one wants oneself
Socio-economic issues
- The cause of decay is socio-economic disputes in the form of contempt of the rich for the poor. The subsequent hatred of the poor, their hope for change that does not come and the lack of community spirit only fuels this
.
This is the start of a scientific and more balanced worldview.
.
Strategy is looking ahead
Two visions that originated in the same era
In Locke, faith and politics remain intertwined. American politicians are (then and now) assumed to be religious.
Spinoza thinks from a different framework. He is in favor of embracing all views, including non-religious, scientific, political, and philosophical ones. According to him, a state religion has negative psychological consequences. Representatives of religion derive too much power from the 'legal' rightness of faith. But no person can completely relinquish their control of judgment.
We have inherited the neoliberal ideology of that time, in particular. This is tough because it will soon be 400 years old.
The world is faced with choices today. The analysis of the Club of Rome, the geopolitical situation, and climate change are not choices but symptoms. The choices are yours.
We will all have to make choices, including in the economic field. Every company and every entrepreneur will have to make choices for themselves.
.
Strategic principles
When I was younger, I was a conjurer. It taught me an important lesson. People are excellent pattern seekers. We spontaneously look for patterns in what we see, hear, feel, in other words, experience. But we have no eye for the principles that cause these patterns. Conjurors make clever use of this for entertainment.
- Conjurors and magicians are the artists of science. Conjurors hide the principles behind the patterns, magicians believe in the patterns
- Science provides insight into the principles that can become economic reality
- Politics determines the frameworks within which these principles may be implemented
- The economy implements these principles within the community
- The community, its culture and art produce conjurors and magicians
Below, I describe three principles (interests, values and goals) that shed light on your strategy.
The first two (interests and values) are intertwined. Even though they are the least ‘practical’, they are still the guiding principles when push comes to shove (regarding your goals).
.
Interests
Steven Fry beautifully describes here how our energy consumption controls our entire being.
.
Fire
I found this incredible and discovered it when I was writing about the beginning of humanity: in Greek mythology, Prometheus—the Titan—makes us out of clay because Zeus is bored. He is the supreme god and has already done everything. He has defeated the Titans and made the world perfect. What else can he do every day?
He wants pets, little creatures to play with, who will worship him, love him, and obey him. He orders Prometheus to make us, the people. Zeus says, "Do what you want." They can travel all over the world, but there is one thing they are not allowed to have: fire.
By fire, Zeus really means fire, which offers us the technology to make iron and bronze, cook, and make small pots. But he also means the divine spark, the fire that makes the gods gods, that makes us creative. Man possesses this spark because Prometheus disobeyed and gave us that spark.
Zeus was furious because, with that spark, humankind would no longer need gods. Then, they would no longer worship him but be autonomous without them.
Stephen Fry – Leuven – March 28th 2025
.
Values
Five value-driven challenges for the near future
The first is financial. Whenever we have had economic problems in the past, instead of tightening our belts, we have always turned on the tap of credit creation and central bank guarantees. The entire world has 350 to 400% debt compared to GDP. We continue to create more and more monetary claims that people think they own as money. The ecological and energetic truth is that they require energy and materials to become reality.
The second is the movement our world is making from a globalised to a multipolar world: Europe, the US, China, Russia, the BRICS countries, Africa, … . How will the raw material pie be divided? Who will pull the monetary and military sheets? Who will be able to go where?
The third is the just-in-time supply chain. Everything you have in your home has already been around the world. Food is produced an average of 2000 km from your plate. We have an incredibly efficient but unfortunately non-resilient system for delivering essential goods and services to people worldwide based on cheap oil, credit and a supposed global peace.
The fourth is the social contract and the trust in cooperation and interaction with the people around you. The power of people lies in their collaboration. Polarisation creates stress in society and makes social contracts difficult. In the past, every village had its village idiot. The community knew him and made sure he was contained. Now, any idiot can use the megaphone of social media to undermine the social cohesion that used to be a warm blanket around him.
The fifth is the imminent total overshoot of the Earth’s carrying capacity. What will we do to manage the Global Commons, such as the atmosphere and oceans, within safe planetary boundaries? Overusing the Global Commons by some and privatising resources endangers their future availability to all. Transgressing planetary boundaries—including climate, biodiversity, and biogeochemical flows—must be avoided to ensure a safe space for humanity.
.
Goals
Making decisions about your strategy
When you choose, you are selecting based on purely personal, unconscious motives. That is what most of us do when we think we are deciding. But a decision is something entirely different. A decision results from a process that considers many possible outcomes; it is the opposite of choosing.
.
Complexity
Let me start with the most used concept of the last years: complexity.
What is the difference between complicated and complex?
- Complicated has a Latin origin: folding. Something that can be folded can be unfolded and then folded back. Think of a difficult origami figure. It simply unfolds back into a sheet of paper
- Complex has a Greek origin that means entanglement. An entangled thing that is taken apart can never be entangled again in the same way
In a complex situation, the interactions are the most important. When interactions evolve favourably, you can give them energy (resources). Conversely, when the interactions are negative, you can reduce your energy on them.
The cookbook metaphor fits in here. A cookbook user follows the recipe, always using the same ingredients and equipment in the same order. A chef is able to combine different ingredients for the dish. He can replace one thing with another in the composition of the dish, and he can adapt the dish to his own context.
What is the difference between systems thinking and complexity thinking?
- Systems thinking tends to define ultimate goals and try to close the gap with them. As a result, many opportunities in the present are missed
- With complexity thinking, you try to describe the present as accurately as possible and then start your strategy with a general sense of direction
Of course, different people perceive the same system differently. What is seen as complex by one person can be clear to another.
However, this does not justify ultra-relativism. Different perspectives do not rule out that a system or situation cannot be methodically investigated and defined. People's perceptions can certainly be tested against this. Whether something is solid, liquid or gaseous can be scientifically determined independently of someone's perceptions.
.
Your strategic action plan
First, describe the present. The 3A principles you can use to describe your current situation are:
Agency
- Who or what can make decisions or has the freedom to act (to what extent)?
The Kodak story is a classic example. The company’s top executives ignored its engineers, who had developed a prototype digital camera, because it would disrupt Kodak’s then-lucrative film business.
.
Affordance
- What opportunities are being offered or held back by the ecosystem of which your company is a part?
The Cambridge Institute for Sustainability Leadership (CISL) puts it this way:
A global industrial and economic transition is underway, restructuring the way economies produce and create value. This shift is being driven by non-negotiable forces: the laws of nature and the limits of planetary carrying capacity.
The direction is clear. The challenge is the pace of change.
Without conscious action to accelerate the transition, the alternative is unmanaged decline. Strategic action can change this trajectory. Those who act now gain a decisive early-mover advantage, set future norms, and influence policy direction and capital flows.
.
Assemblage (the totality of the previous two)
- What are the (cultural) patterns in your organization that constrain or stimulate behaviour?
On the one hand, the level of competence to act of your people can make a clear difference. On the other hand, your board can do something that a middle manager cannot do, that a front-desk employee cannot do, etc. Different parts of your organization may be in various situations and have different trajectories to follow.
But be careful when you surround yourself with people who (re)tell your stories to counteract this. What happens is that these stories start to pile up. They acquire a material reality, which can create downward causality.
.
Second, choose a direction
We all know the metaphor of the North Star. I want to place another metaphor next to it. The arrow that points the way to Brussels never goes to Brussels itself. What’s more. If you follow the arrow, let’s say, in a northeast direction, you will probably find an arrow to Brussels that points you east, only to find one that points west …
This means that your strategic path does not always follow the direction that your goal initially indicates. You need this flexibility without losing sight of the general direction.
.
So here we are, what to do now?
The core of what you should do now is very simple:
- You start by determining what is not possible
- Then, within this constraint, you identify your constructors that can perform tasks repeatedly and consistently
Constructors are “your decisions that make future decisions possible”, shaping your future reality. We are not talking about operational tasks here, but about cognitive activation, processes and cultures.
You can mold your constructors according to a neoliberal model or you can view them through Spinoza’s lens.
We are at a crossroads together. May I ask you to read the bullet point again? And then decide.
.
.
Sources
- Eleanor Stratton - Locke’s Influence on the Constitution - in Constitutional Topics - 2024
- Ethica van Spinoza - vertaald door D. Burger
- Door Spinoza’s lens – Tinneke Beeckman
- Stephen Fry
- Nate Hagens
- Cynefin Co
- Cambridge Institute for Sustainability Leadership (CISL)
.
Creating strategies
.
This is part of the abstract of a recent article on 'foresight', which you can translate here as 'long-term thinking':
.
Systematizing corporate foresight and integrating it into decision-making is critical to harness its value. However, many companies face challenges due to limited legitimacy, leading to scarce resources and a lack of commitment. Previous research has paid little attention to various ways to develop foresight capability, particularly at the intermediate stage of foresight maturity, where legitimacy is often lacking. We address this issue by exploring alternative organizing models to demonstrate foresight's value within firms. We conceptualize a corporate foresight system (CFS) comprising structures, roles, and activities for managing futures knowledge.
.
Note (in the illustration) that 'long-term thinking' is not a linear process, but has 'loops' running in both/opposite directions.
The full article is open access and can be found here:
| Four archetypes of organizing corporate foresight at the intermediate maturity stage: A multiple case study - Technological Forecasting and Social Change - 2025 |
|---|
| https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0040162525001489#f0015 |
.
About those who create strategies
.
| Adam Grant |
|---|
|
.
| A Beautiful Question - Frank Wilczek - 2015 |
|---|
In order to begin computing the world’s behaviour using (the) dynamical equations, you must first specify the state of the world at one time, as input. (Of course, if you ‘re interested in something smaller than the whole world, and you can effectively isolate it from the rest, you only need to know the state of your subsystem.)We have an excellent theory for the later. But only empirical observations and incomplete, more or less plausible speculations, regarding the former. |
.
| John Maynard Keynes |
|---|
| The master-economist must possess a rare combination of gifts .... He must be mathematician, historian, statesman, philosopher -- in some degree. He must understand symbols and speak in words. He must contemplate the particular, in terms of the general, and touch abstract and concrete in the same flight of thought. He must study the present in the light of the past for the purposes of the future. No part of man's nature or his institutions must be entirely outside his regard. He must be purposeful and disinterested in a simultaneous mood, as aloof and incorruptible as an artist, yet sometimes as near to earth as a politician. |
.
The value of synthesis is rising fast. In a world of information abundance, the edge belongs to those who can move across domains - linking ideas, exposing blind spots, and seeing principles, patterns, systems where others see silos. Not the hyper-specialist, stuck in the weeds. It demands the kind of mind that can sit at the intersection of disciplines - philosophy to ask what matters, ethics to guide what we should do, psychology to understand how people behave and trust, sociology to see second-order consequences.
.
It’s the hardest skill. Synthesis is where depth meets discernment. Where information becomes insight. Where expertise becomes wisdom. And that, more than anything, is what separates us from the machine. Where we can strategize to weigh trade-offs and navigate complexity.
.
Corporate futuring: an overview
.
You'll find more in depth information on all Corporate futuring topics on the following pages. Chapter 4 of your Business Acumen is entirely devoted to Corporate futuring.
.
| What is Complexity Informed Strategy? |
|---|
| https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=o-gOyaXZLqo |
.
Your corporate futuring path
.
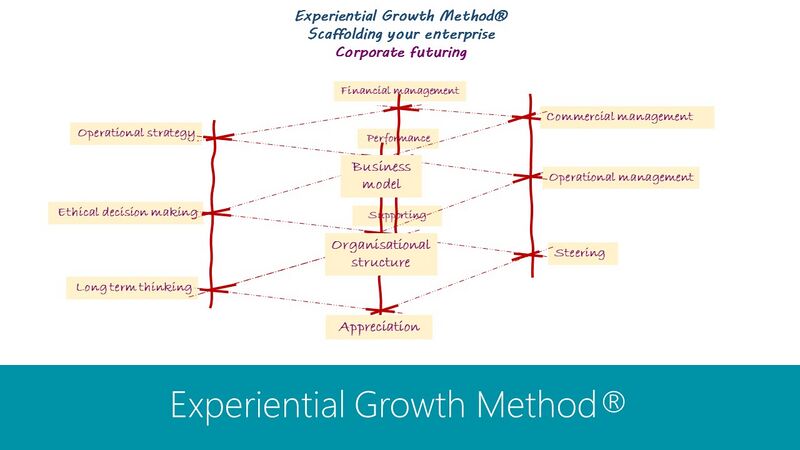
Corporate futuring is about creating and maintaining your long term strategy. It consists in the first place of 'Long-term Thinking', 'Ethical Decision-making', and your 'Operational strategy':
- The core of Corporate futuring is helping you to make those decisions that enable future decisions
- The decisions of the past created the position you are in today
- 'Now' is the moment to make those decisions that will shape your future
- Decisions who have the highest probability to create value for all stakeholders
.
Three distinct steps to go
.
- Where are we now?
- Which direction(s) can we go?
- What is the next step to take?
.
Below on this page you'll find more info about all elements involved.
On the next pages we dive deeper into value realisation, emerging results, the strategic cycle and methods to take action.
The three core questions are always leading. When what to use depends on your situation and the context your business is in.
.
Defining the strategy concept
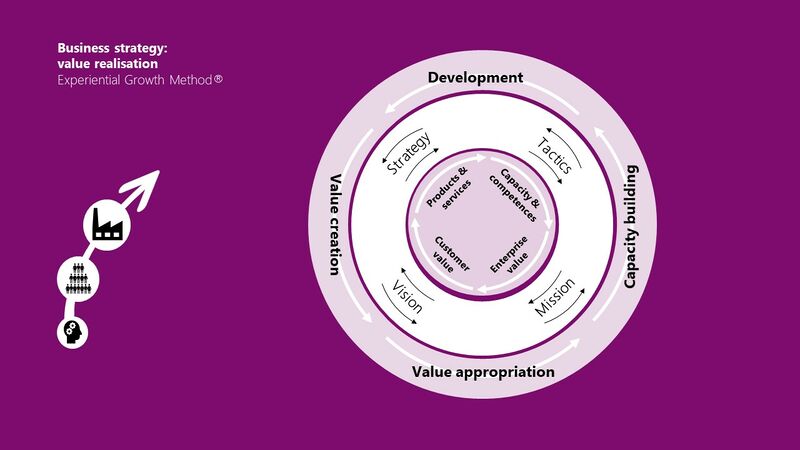
Strategy has a double meaning. On the one hand, it encompasses the entire strategic process. On the other hand, it is the second of the four strategic steps: Vision, Strategy, Tactics and your Mission.
.
"Strategy (as the process) is making those decisions that enable future decisions" - S. Vermeylen
Not making decisions is, by definition, leaving the critical decisions for you and your business to the context in which you operate.
If it works out well for you, you're in luck. If not, you're out of luck. Therefore, it is better to make strategic decisions.
They are not the decisions you make to take operational actions tomorrow but those that make it possible to make correct, or even better, operational decisions in the foreseeable future.
Strategy is - parallel to your financial investment - the mental investment you and your employees make to improve your assets, structures, human capital, resources, customer portfolio, goods and/or service offerings. In short, strategy matters most to your business in order to enhance and grow.
.
Your enterprise core strategy consists of:
- Long Term Thinking
- The decisions of the past created the position you are in today: NOW
- Ethical Decision Making
- 'Now' is the moment to make those decisions that will shape your future: DIRECTION
- Operational strategy
- Make the decisions that have the highest probability to realise value: THE NEXT STEP
.
The situations where Corporate futuring offers you an answer
If you are an entrepreneur, a start-up, a scale-up, an sme with big ambitions, or if you are right in the transition phase between generations, a more subtle situation dictates your need for strategic thinking:
- a changing context (aka market situation)
- an uncertainty about being in a transition phase (not knowing what it will take and lead to)
- a feeling of being at the top of a prosperous area (the famous S-curve), it can only go down
- a need for new beginning (organisational innovation, product- and/or service innovation)
- a feeling of becoming obsolete
- ...
.
Triggers leading towards the need for a new Operational Strategy
First and foremost, your business operates in its context:
- changes in your market force you to choose a new path
- the shortage in the labour market. The number of employees forces you to review your processes and, therefore, also your strategy
- the social revolution towards a green economy. New ways of working ask for new ways of strategising: ESG
- changes in your market force you to choose a new path
- changes or transitions in your organisational structure necessitate a new strategy
- ...
.
Core questions to start creating direction
.
- Why are you in the situation you are in?
- In what direction do you want to evolve?
- How do you see the future for your business and your company?
- How can you use our scarce resources for the best future?
- What is the next (correct) step that you should take now?
.
Your strategies for creating value
Directions to go, who create value for all, are nuanced:
.
Operational excellence (providing services)
- In search of risk reduction, leading towards the substrategy 'The efficiency leader'
- Mastering emotional evaluation, leading towards the substrategy 'The customer leader'
Customer intimacy (mastering emotional relationships)
- Empathic (emotional) evaluation, leading towards the substrategy 'The client expert'
- Attention to greater interests, leading towards the substrategy 'The authority'
Product leadership (providing better services)
- Empathic (emotional) evaluation, leading towards the substrategy 'The ecosystem builder'
- Attention to greater interests, leading towards the substrategy 'The serial disruptor'
.
Your goal of Corporate futuring: value realisation by emerging results
.
.
The one thing your (operational) strategy has to deliver is value for all stakeholders.
But, as you may have experienced, value realisation isn't a walk in the park. It is about connecting all the dots. Value creation leads to the emergence of results.
However, these results are not immediate. They only manifest when multiple elements within your organisation are connected and guided by your vision, strategy, tactics, and mission, all within the framework of Long-term thinking, Ethical decision-making, and Operational strategy. The Experiential Growth Method® defines these 'vertical related' action fields as part of the implementation of your Corporate futuring:
.
- Reputation
- Operational strategy (strategic doing)
- Ethical decision making
- Long term thinking
- Culture
- Business model
- Organisational structure
- Appreciation
- Profit
- Financial management
- Performance
- Supporting
- Revenue
- Commercial management
- Operational management
- Steering
.
The dynamics of Corporate futuring: your strategic thinking and doing
.
.
Your strategic cycle (vision, strategy, tactics, mission) mitigates the outside and inside forces of your enterprise and unites them for value realisation.
.
How to succeed
As human beings
As human beings, we all need three things to succeed.
- First of all, enough food and shelter
- Secondly, a mate to reproduce
- Thirdly, information about the world surrounding us.
We all need this information to move towards enough resources, select the right fellow humans and create our habits and processes to be able to develop in our environment.
.
As an enterprise
This applies to your enterprise in the very same way:
So, the first question we can ask ourselves concerns our resources.
- Why is there an opportunity to invent / advance / grow now?
- And what patterns arise from the interests our business has?
.
The second one is about evaluating our surroundings.
- How / with whom will we make this opportunity work?
- And what principles do we organise our enterprise from, startign with our company's values?
.
The third one concerns information.
- What drives the use of our value proposition?
- And what are the human-based processes we create from the goals our enterprise wants to realise?
.
Some iconic examples
Computer
- Why became the computer industry possible?
- The silicon transistor.
- How was this opportunity reformed?
- Memory storage, first magnetic tape, later solid-state.
- What made the computer industry big?
- Software.
.
Logistic chain
- Why became the logistic chain possible?
- The platform economy.
- How was this opportunity reformed?
- www - ai - 5G.
- What made the logistic chain big?
- Need for predictable, transparent supply chains.
.
The enterprise elements of the Corporate futuring framework
.
.
The Experiential Growth Method®, defines all these action fields as part of Corporate futuring.
Their 'horizontal' relationships provide the processes in your organisation that create a natural (corporate) culture and a wanted strategy.
.
- Outer focus
- Operational strategy (strategic doing)
- Business model
- Financial management
- Commercial management
- Other focus
- Ethical decision making
- Organisational structure
- Performance
- Operational management
- Inner focus
- Long term thinking
- Appreciation
- Supporting
- Steering
.
Your STRATEGY, consists of your vision, strategy, tactics and your mission
.
1. The elements of your VISION you can explore:
Customer strategy: value proposition
- How do you turn the world upside down?
- What will your customer really miss if he does NOT purchase your product or service?
.
Positioning strategy: market position
- How much are we
- Task drive ← vs.→ Market driven
- Product driven ← vs. → Capacity driven
.
2. The elements of value STRATEGY you can explore:
Steering concepts
- Capital
- Resources
- Capabilities
- People
- Competencies
.
Context strategy: your relational position
- ESG
- Environmental
- Social
- Governance
- STEEPLE
- Social
- Technological
- Economic
- Environmental
- Political
- Legal
- Ethical
- Client experiences
- Stakeholder analysis
- Competition analysis
- Employee experiences
.
3. Elements of your TACTICS you can explore
Business model strategy
- Building on market context (see vision & strategy)
- Business model → Value realisation
- Value proposition
.
4. Elements of your MISSION you can explore
Scenarios
From your big dream via feasible scenarios to concrete goals.
This is the moment where the difference between development and execution becomes relevant.
- Development is concerned with exploring the “unknown unknowns” through possible futures (from incremental to disruptive)
- Scenarios and business dynamics modeling translate these insights into an executable plan (now known unknowns)
.